Description
Características
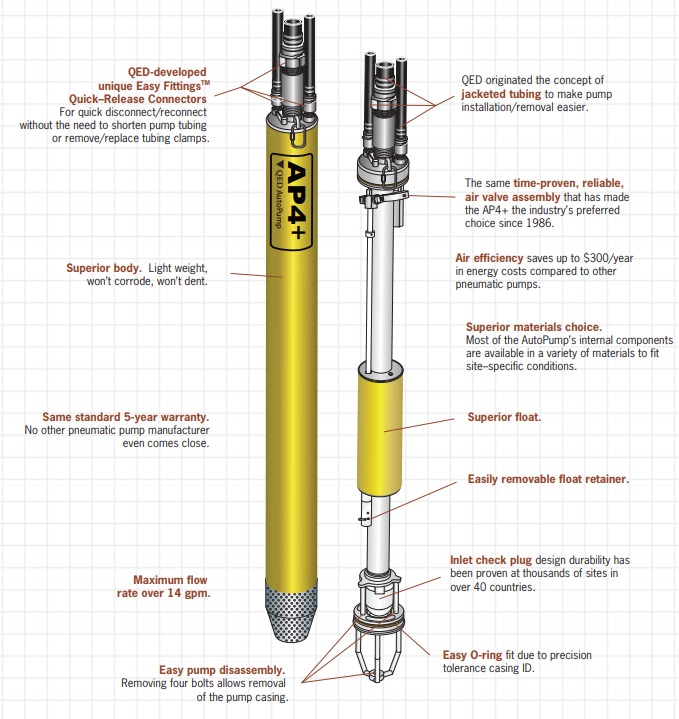
The AutoPump AP4 + are ATEX certified for Zone 0.
- Pump provides positive air displacement with top and bottom fill design.
- Short and long lengths meet different job requirements.
- The product can be used from approximately 90 meters.
- 5 years warranty.
The pump is complemented by the most comprehensive selection of accessories to provide a complete system that meets specific site requirements.
AutoPump pumps are constructed of improved materials to further extend the life of the pump and expand the range of conditions in which each model is used.
The AP4 + is part of the AutoPump family of original automatic pumps, which were developed in the mid-1980s specifically for unique pumping needs in remediation and landfills. Air-powered AutoPumps are proven worldwide at thousands of remediation sites and landfills. This is what makes AutoPumps the number one choice of environmental professionals thanks to their reliability, durability, performance range, and technical support.
Tailored advisory service according to the type of pollutant, type of project and characteristics of the installation. We offer the complete installation and commissioning service of a complete ATEX system and data management system.
Contact us envirotecnics@envirotecnics.com or Tel: +34 872 080 542.
Functioning
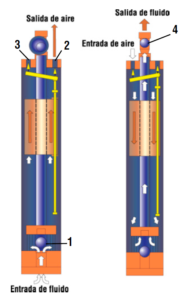
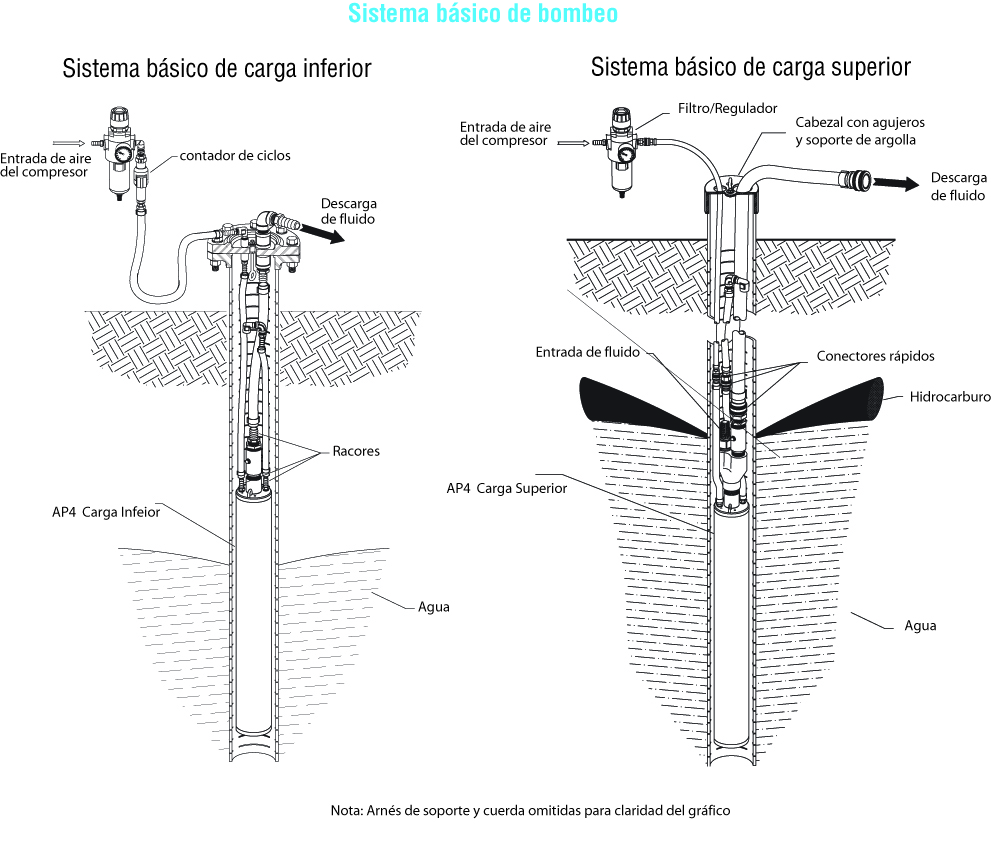
Fill cycle
The fluid enters the pump body by gravity, pushing the suction valve (1). The air release valve (2) is open to allow air to evacuate while the pump is filling. In maximum position, the float drives a mechanism that simultaneously triggers the closing of the exhaust valve and the opening of the compressed air valve (3).
Empty cycle
The increase in pressure in the body of the pump causes the closing of the suction valve (1) and the expulsion of the liquid towards the network via the check valve (4). The return of the float to the low position triggers, unlike before, the closing of the compressed air valve (3) and the opening of the air release valve (2). From then, a new cycle would begin.
This mechanical operation does not consume compressed air in the absence of fluid to pump.
El regreso del flotador a la posición baja desencadena, al contrario que anteriormente, el cierre de la válvula de aire comprimido (3) y la apertura de la válvula de escape de aire (2).
A partir de entonces se iniciaría un nuevo ciclo.
Este funcionamiento mecánico no consume aire comprimido en ausencia de fluido para bombear.
Aplicaciones
Limits of applications
- Maximum Temperature: 82 ° C (180 ° F)
- PH range: 4-9
- Solvents and Hydrocarbons: Gasoline,
- diesel, JP1-JP6, BTEX, MTBE, Leachate
Optional (depending on connection and availability):
- Quick connector kits in brass or stainless steel
- Hose and pipe connection kits.
- Conversion kits top loading to bottom and vice versa
Pipeline
- We have the necessary pipes and connections.
Rental
- We have these pumps for rent.
Applications:
Advantages
- Great flow and pumping capacity.
- Easy to disassemble and clean.
- Patented design offering proven performance, durability and reliability.
- Withstands certain solids, solvents, hydrocarbons, and corrosive conditions beyond the limits of electric pumps.
Depending on the model, the pumps are designed for great pumping challenges with:
- Hydrocarbons
- Solvents
- Suspended solids
- Leachate
- Extreme temperatures
- Viscous liquids
- Frequent stop and start cycles